Strained Ties: Analyzing The Breakdown In U.S.-China Relations And The Risk Of Cold War

Table of Contents
Historical Context: From Détente to Discord
Understanding the current state of U.S.-China relations requires examining their historical evolution. The relationship between the United States and China has been a rollercoaster ride, marked by periods of cooperation and intense conflict. The establishment of diplomatic ties in 1979 marked a pivotal moment, ushering in an era of engagement and economic interdependence. This period saw significant growth in bilateral trade and investment, fueling China's economic ascent and integrating it into the global economy. However, this seemingly harmonious period masked underlying tensions.
- Early engagement and economic interdependence: The initial years were characterized by a cautious approach, with both nations seeking economic benefits and strategic advantages. The U.S. saw a potential market in China, while China benefited from access to Western technology and investment. This period saw significant growth in Sino-American trade relations.
- Shifting geopolitical dynamics and rising Chinese power: As China's economic and military power grew, so did its ambitions on the global stage. This rise, coupled with differing geopolitical visions, created friction in the relationship. The evolution of U.S.-China trade shifted from mutual benefit to intense competition.
- Key turning points in the relationship: Several key events exacerbated existing tensions. These include the 1989 Tiananmen Square protests, which strained relations, the 2001 accession of China to the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the more recent trade disputes initiated by the Trump administration. The South China Sea dispute also significantly impacted U.S.-China diplomatic history, highlighting a growing divergence in interests.
Key Drivers of the Current Strained Relationship
The current deterioration in U.S.-China relations is multifaceted, stemming from a convergence of economic, geopolitical, and ideological factors.
Trade Wars and Economic Competition
The ongoing trade war, characterized by reciprocal tariffs and restrictions, has significantly damaged U.S.-China trade relations. This economic conflict is fueled by accusations of unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and the ambition of China to dominate key technological sectors.
- Examples of specific trade disputes: The dispute over agricultural products, steel and aluminum tariffs, and restrictions on technology transfer highlight the depth of the economic conflict. The consequences include disruptions to global supply chains, increased costs for consumers, and a chilling effect on foreign direct investment.
- Intellectual property rights: China's record on intellectual property rights has been a major point of contention, leading to allegations of theft and forced technology transfer. This economic conflict directly impacts U.S.-China relations.
Geopolitical Rivalry and Strategic Competition
The competition for global influence has intensified, with both the U.S. and China vying for strategic advantage in regions such as the South China Sea, Africa, and the Indo-Pacific. Military buildup, cyber warfare, and the formation of competing alliances further fuel this rivalry.
- Examples of specific geopolitical clashes: The disputes in the South China Sea, Taiwan Strait tensions, and the competition for influence in Africa represent key areas of friction. The military buildup by both nations has increased the risk of miscalculation and accidental conflict. The involvement of other nations further complicates the situation.
- Alliances and partnerships: Both countries are actively forming alliances and partnerships, further intensifying the geopolitical competition. This creates a complex web of relationships that influence the overall dynamic of U.S.-China relations.
Ideological Differences and Human Rights Concerns
Fundamental differences in political systems and human rights records contribute to the strained relationship. The U.S. criticism of China's human rights record, particularly concerning Xinjiang, Tibet, and Hong Kong, creates a significant barrier to improved relations.
- Examples of human rights concerns in China: Concerns about human rights violations in Xinjiang, the suppression of dissent in Hong Kong, and the lack of political freedoms fuel tensions. These concerns have led to sanctions and diplomatic pressure from the United States.
- Impact on bilateral relations: The differing perspectives on human rights create a fundamental obstacle to improved relations. This creates a fundamental disconnect in U.S.-China relations.
Assessing the Risk of a New Cold War
The current trajectory of U.S.-China relations raises legitimate concerns about the potential for a new Cold War. While the specifics differ from the original Cold War, the parallels are striking.
- Comparison of military capabilities and strategies: Both nations possess significant military capabilities, with advanced weaponry and strategies designed for potential conflict. The increased military spending and development of advanced weapons systems raise the stakes considerably.
- Analysis of the potential for proxy conflicts: The risk of proxy conflicts in various regions is high, as both countries vie for influence through support of different factions and regimes. This could easily escalate into direct conflict.
- The role of alliances and international institutions: The formation of competing alliances and the weakening of international institutions could exacerbate tensions and make de-escalation more difficult. This could lead to a fragmented global order and potentially lead to armed conflict.
Potential Pathways to De-escalation and Improved Relations
Despite the current tensions, there are potential pathways towards de-escalation and improved U.S.-China relations.
- Diplomacy and dialogue: Renewed diplomatic engagement and high-level talks are essential for managing disagreements and preventing misunderstandings. Open communication channels are crucial to avoid miscalculation.
- Cooperation on global challenges: Collaboration on shared challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and global health security can foster trust and mutual understanding. Addressing these issues collaboratively could create opportunities for cooperation.
- Establishing clear rules and norms for competition: The development of clear rules and norms for economic and geopolitical competition can help to reduce the risk of conflict and promote a more stable and predictable relationship. Establishing clear norms could alleviate the uncertainty inherent in great power competition.
Conclusion: Navigating the Perilous Path of U.S.-China Relations
The deteriorating U.S.-China relationship presents a complex and perilous path. The risk of a new Cold War, or even worse, direct military conflict, is undeniably real. The interwoven nature of economic, geopolitical, and ideological factors makes this a particularly challenging issue to address. Understanding the intricate dynamics of U.S.-China relations is crucial for navigating the path ahead. Continue learning about the challenges and opportunities involved in this vital relationship, and advocate for policies that foster stability and prevent a new Cold War. Engaging in informed discussions and supporting initiatives that promote peaceful coexistence and cooperation between the U.S. and China are critical steps toward mitigating this significant global risk. The future of global stability hinges, in part, on a constructive resolution of these crucial Sino-American relations.

Featured Posts
-
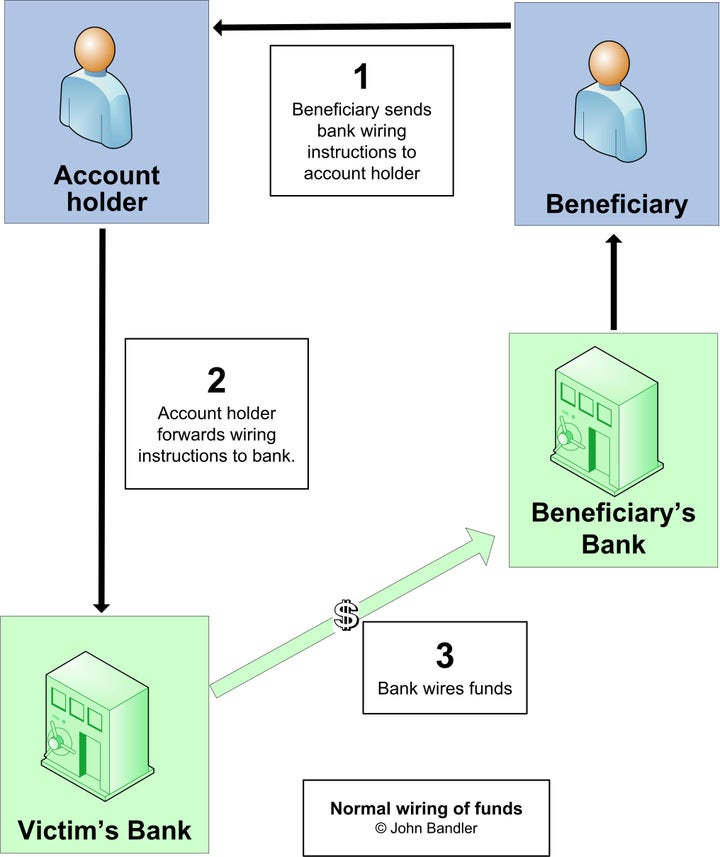 Office365 Data Breach Inside The Millions Dollar Cybercrime Scheme
Apr 22, 2025
Office365 Data Breach Inside The Millions Dollar Cybercrime Scheme
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Razer Blade 16 2025 Review Ultra Portable Powerhouse Or Overpriced Luxury
Apr 22, 2025
Razer Blade 16 2025 Review Ultra Portable Powerhouse Or Overpriced Luxury
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Enhanced Security Collaboration China And Indonesia Forge Closer Bonds
Apr 22, 2025
Enhanced Security Collaboration China And Indonesia Forge Closer Bonds
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Sweden And Finlands Military Integration A Pan Nordic Defense Strategy
Apr 22, 2025
Sweden And Finlands Military Integration A Pan Nordic Defense Strategy
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Trade War Concerns Dow Futures And Dollar React Live Market Analysis
Apr 22, 2025
Trade War Concerns Dow Futures And Dollar React Live Market Analysis
Apr 22, 2025
