The Grim Truth About Retail Sales: What It Means For Canadian Interest Rates
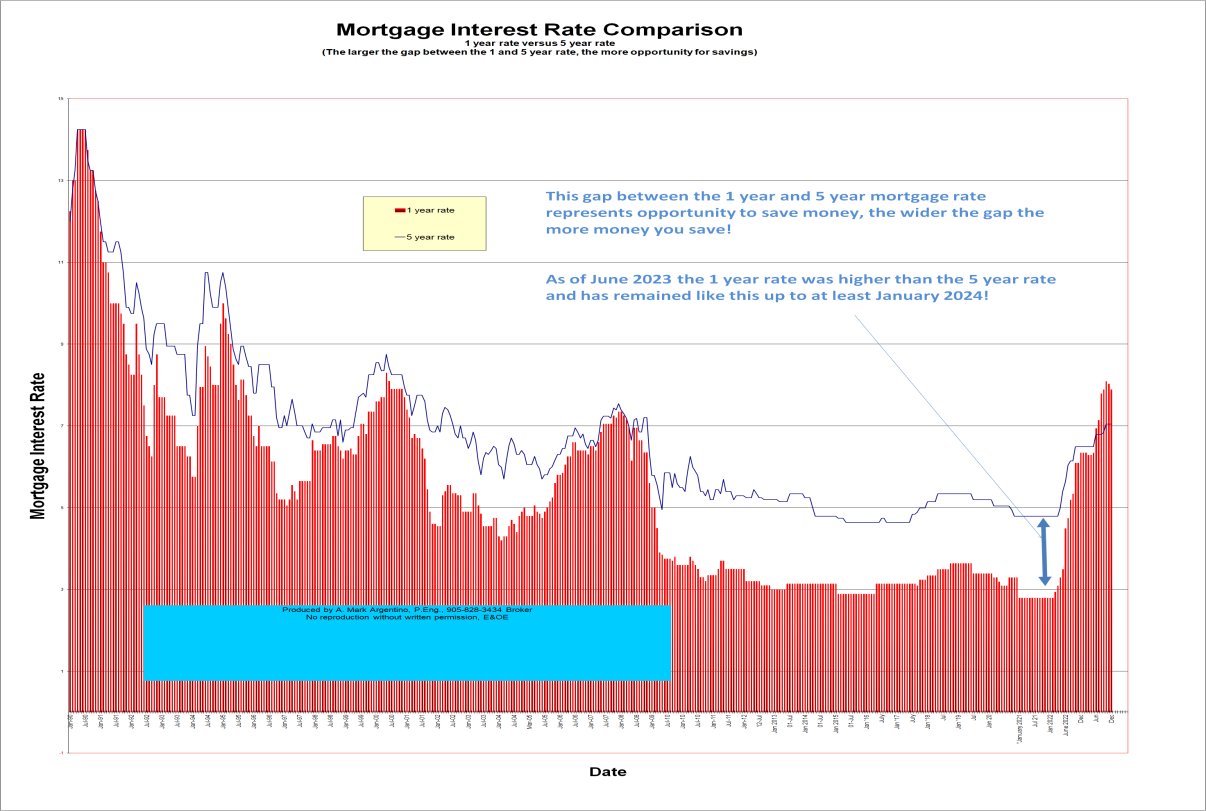
Table of Contents
Weak Retail Sales: A Sign of Economic Slowdown in Canada
The recent downturn in retail sales signifies a broader economic slowdown within Canada. Several factors contribute to this decline, impacting consumer spending and overall economic health.
Declining Consumer Spending
Several interconnected factors are squeezing consumer spending power:
- High Inflation: Soaring inflation continues to erode purchasing power, forcing consumers to cut back on non-essential spending. The persistent increase in the cost of living, particularly for food and energy, leaves less disposable income for discretionary purchases.
- Rising Interest Rates: The Bank of Canada's efforts to combat inflation through interest rate hikes have increased borrowing costs. This makes it more expensive to finance purchases, leading to reduced consumer borrowing and a potential increase in household debt burden.
- Geopolitical Uncertainties: Global uncertainties, including the ongoing war in Ukraine and supply chain disruptions, contribute to consumer anxiety and a reluctance to spend. This uncertainty fuels a wait-and-see attitude, delaying major purchases.
- Declining Sales Across Sectors: Specific sectors are experiencing significant drops. For example:
- Clothing sales have fallen by an average of 5% in the past quarter.
- Electronics sales are down 8%, reflecting a slowdown in consumer electronics upgrades.
- Furniture sales have decreased by 3%, indicating a cooling housing market and reduced demand for home furnishings.
Impact on GDP Growth
Retail sales are a significant component of Canada's GDP (Gross Domestic Product). A decline in retail spending directly translates to slower GDP growth. Statistics Canada's data clearly shows a strong correlation between these two factors. Continued weakness in retail sales increases the probability of a recession, triggering a ripple effect across various sectors. Industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and logistics, heavily reliant on consumer demand, will face reduced activity and potential job losses.
The Bank of Canada's Response: Interest Rate Adjustments
The Bank of Canada plays a vital role in managing the Canadian economy. Its mandate includes achieving price stability and full employment – a challenging balancing act, especially in the current environment.
The Bank of Canada's Mandate
The Bank of Canada aims to keep inflation within its target range (1-3%) while promoting sustainable economic growth and full employment. Weakening retail sales complicate this task, forcing the Bank to consider various approaches.
Interest Rate Hikes and Their Implications
The Bank of Canada has recently increased interest rates to combat inflation. While these hikes aim to curb inflationary pressures, they also have negative consequences:
- Increased Borrowing Costs: Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers, potentially impacting investment and consumer spending further.
- Reduced Investment: Businesses may postpone expansion plans due to higher borrowing costs, leading to slower economic growth.
- Current Interest Rate and Future Adjustments: The current overnight rate stands at [insert current interest rate]. Further adjustments will heavily depend on future retail sales data and other economic indicators. A continued decline in retail sales could lead to a pause or even a potential reduction in future rate hikes.
Balancing Act: Inflation vs. Economic Growth
The Bank of Canada faces the difficult task of balancing the need to control inflation with the need to avoid stifling economic growth. Weak retail sales complicate this balancing act, necessitating careful consideration of the potential impacts of any interest rate decision.
Forecasting Future Trends: Retail Sales and Interest Rates
Predicting future trends requires a comprehensive analysis of various economic indicators beyond just retail sales.
Analyzing Economic Indicators
The Bank of Canada considers a range of indicators, including:
- Employment Data: Job growth and unemployment rates provide insights into consumer confidence and spending potential.
- Inflation Rates: The pace of inflation significantly influences consumer spending and the Bank of Canada's policy response.
- Housing Market Data: The housing market's health impacts consumer confidence and spending, particularly on durable goods.
Expert Opinions and Predictions
Economists and financial analysts hold diverse views on future retail sales and interest rate trajectories. Some predict a continued slowdown, potentially necessitating further rate hikes to curb inflation. Others believe the economy is nearing a bottom, and retail sales may start to recover, allowing for a pause or even a rate cut.
Potential Scenarios
Several scenarios are possible:
- Optimistic Scenario: Retail sales gradually recover, inflation eases, and the Bank of Canada pauses interest rate hikes or even implements a small cut.
- Pessimistic Scenario: Retail sales continue to decline, inflation remains stubbornly high, forcing the Bank of Canada to implement further and potentially more aggressive rate hikes, potentially triggering a recession.
Conclusion: Understanding the Interplay Between Retail Sales and Canadian Interest Rates
Weak retail sales are a significant indicator of economic health in Canada, having a direct impact on the Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions. Monitoring these figures is crucial for understanding the direction of the Canadian economy. The interplay between these two factors is complex, demanding careful analysis of various economic indicators and expert opinions.
To stay informed about the evolving situation regarding Canadian interest rates and retail sales, subscribe to our newsletter, follow reputable financial news sources, and consider consulting a financial advisor to understand how these factors might impact your personal finances. Understanding the relationship between fluctuating retail sales and Canadian interest rates is essential for navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Wallaces Take Challenging The Nascar Norm
Apr 28, 2025
Wallaces Take Challenging The Nascar Norm
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Can Perplexity Beat Google Its Ceo On The Upcoming Ai Browser Revolution
Apr 28, 2025
Can Perplexity Beat Google Its Ceo On The Upcoming Ai Browser Revolution
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Record Breaking Year For Abu Dhabi 26 2 Billion Real Estate Boom And Major Infrastructure Investments
Apr 28, 2025
Record Breaking Year For Abu Dhabi 26 2 Billion Real Estate Boom And Major Infrastructure Investments
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Aaron Judges Lineup Spot Will Boones Decision Satisfy The Star
Apr 28, 2025
Aaron Judges Lineup Spot Will Boones Decision Satisfy The Star
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Doris Burke Earns Praise From Dwyane Wade For Thunder Timberwolves Game Analysis
Apr 28, 2025
Doris Burke Earns Praise From Dwyane Wade For Thunder Timberwolves Game Analysis
Apr 28, 2025
