Assessing The Risk: Tariffs And China's Export-Driven Growth
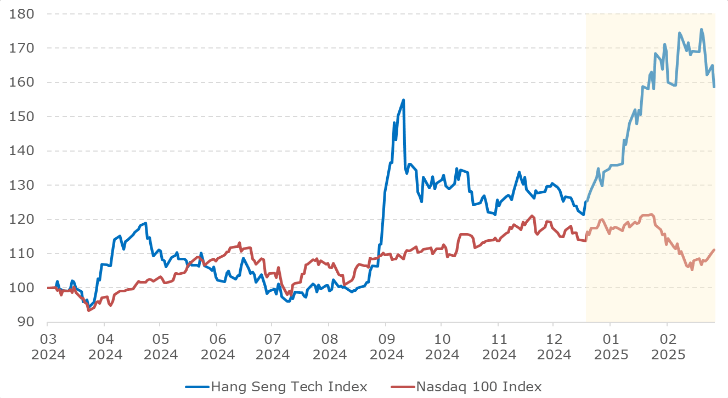
Table of Contents
The Direct Impact of Tariffs on Chinese Exports
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, directly increase the cost of Chinese goods in international markets. This increased cost reduces the competitiveness of Chinese products compared to those from countries not subject to the same tariffs. The US-China trade war, for example, highlighted this impact dramatically. The imposition of import tariffs by the US led to a noticeable decline in certain sectors of Chinese exports.
- Increased prices for Chinese goods in target markets: Higher tariffs mean consumers in importing countries pay more for Chinese products, reducing demand.
- Reduced demand for Chinese products due to higher prices: This decrease in demand directly translates to lower export volumes for Chinese businesses.
- Shifting of global supply chains away from China: Businesses seek alternative suppliers in countries with lower tariff barriers, disrupting established supply chains.
- Examples of specific tariffs and their impact on particular Chinese export sectors: Tariffs on technology products, for example, significantly impacted Chinese tech companies' ability to compete in the global market. Similarly, tariffs on manufactured goods reduced the competitiveness of Chinese manufacturers in various sectors.
Indirect Economic Consequences for China
The impact of tariffs on Chinese exports isn't limited to the export sector itself. The ripple effects extend throughout the entire Chinese economy, creating significant indirect consequences. Reduced export revenue leads to a slowdown in overall economic growth, impacting various sectors.
- Reduced economic growth rates due to lower export revenue: A decline in exports directly impacts GDP growth, potentially leading to slower economic expansion.
- Potential job losses in export-oriented industries: Businesses facing reduced demand may resort to layoffs or cutbacks, leading to unemployment in export-dependent sectors.
- Impact on domestic investment and consumption: Slower economic growth discourages investment, and reduced consumer confidence may lead to lower spending, creating a downward spiral.
- Increased inflationary pressures due to supply chain disruptions: Shifting supply chains can cause shortages and price increases for certain goods, leading to inflation.
China's Response to Tariff Pressures
Facing these challenges, China has implemented several strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of tariffs and maintain its economic growth. These strategies focus on diversifying its economic activities and reducing reliance on exports.
- Focus on developing domestic markets and reducing reliance on exports: China is actively promoting domestic consumption to lessen its dependence on export-led growth.
- Investment in technological innovation to enhance competitiveness: Investment in R&D and technological advancements aims to increase the competitiveness of Chinese products in the global market.
- Strategic alliances and new trade agreements with other countries: China is actively forging new trade partnerships with countries less affected by the tariff disputes, diversifying its export markets.
- Expansion of the Belt and Road Initiative to secure new markets: The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) plays a crucial role in this strategy by creating new trade routes and infrastructure projects, opening up new markets for Chinese goods.
The Role of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
The BRI is a significant component of China's response to tariff pressures. By investing in infrastructure projects and fostering economic cooperation across Eurasia and beyond, the BRI aims to create new trade routes and access to diverse markets, reducing reliance on traditional export destinations. This diversification of trade routes mitigates the risk associated with reliance on any single market. The BRI also promotes economic growth in participating countries, creating potential new customers for Chinese goods and services.
Long-Term Implications for Global Trade
The tariff disputes and their impact on China's export-driven growth have significant implications for global trade patterns, economic stability, and geopolitical relationships.
- Increased uncertainty and instability in global markets: Trade wars and tariff disputes create uncertainty, making businesses hesitant to invest and impacting global economic stability.
- Potential for further escalation of trade tensions: The current situation highlights the potential for further escalation of trade conflicts, creating a more fragmented and less interconnected global economy.
- Long-term implications for global supply chains and economic growth: The disruption of supply chains and the potential for a more protectionist global trade environment have long-term consequences for global economic growth.
Conclusion
The increasing prevalence of tariffs poses significant risks to China's export-driven growth model. We've explored the direct and indirect economic consequences, ranging from reduced export revenue and job losses to inflationary pressures and slower GDP growth. China's response, including the focus on domestic markets, technological innovation, and the Belt and Road Initiative, demonstrates its proactive efforts to mitigate these risks. However, the long-term implications for global trade remain uncertain, highlighting the need for careful analysis and proactive strategies. Understanding the risks associated with tariffs is crucial for navigating the complexities of China's economic future. Continue to assess the risk and stay informed about the latest developments in China's export-driven growth and the impact of tariffs on its economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Jan 6 Hearing Witness Cassidy Hutchinson To Publish Memoir This Fall
Apr 22, 2025
Jan 6 Hearing Witness Cassidy Hutchinson To Publish Memoir This Fall
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Where To Start A Business A Map Of The Countrys Best Locations
Apr 22, 2025
Where To Start A Business A Map Of The Countrys Best Locations
Apr 22, 2025 -
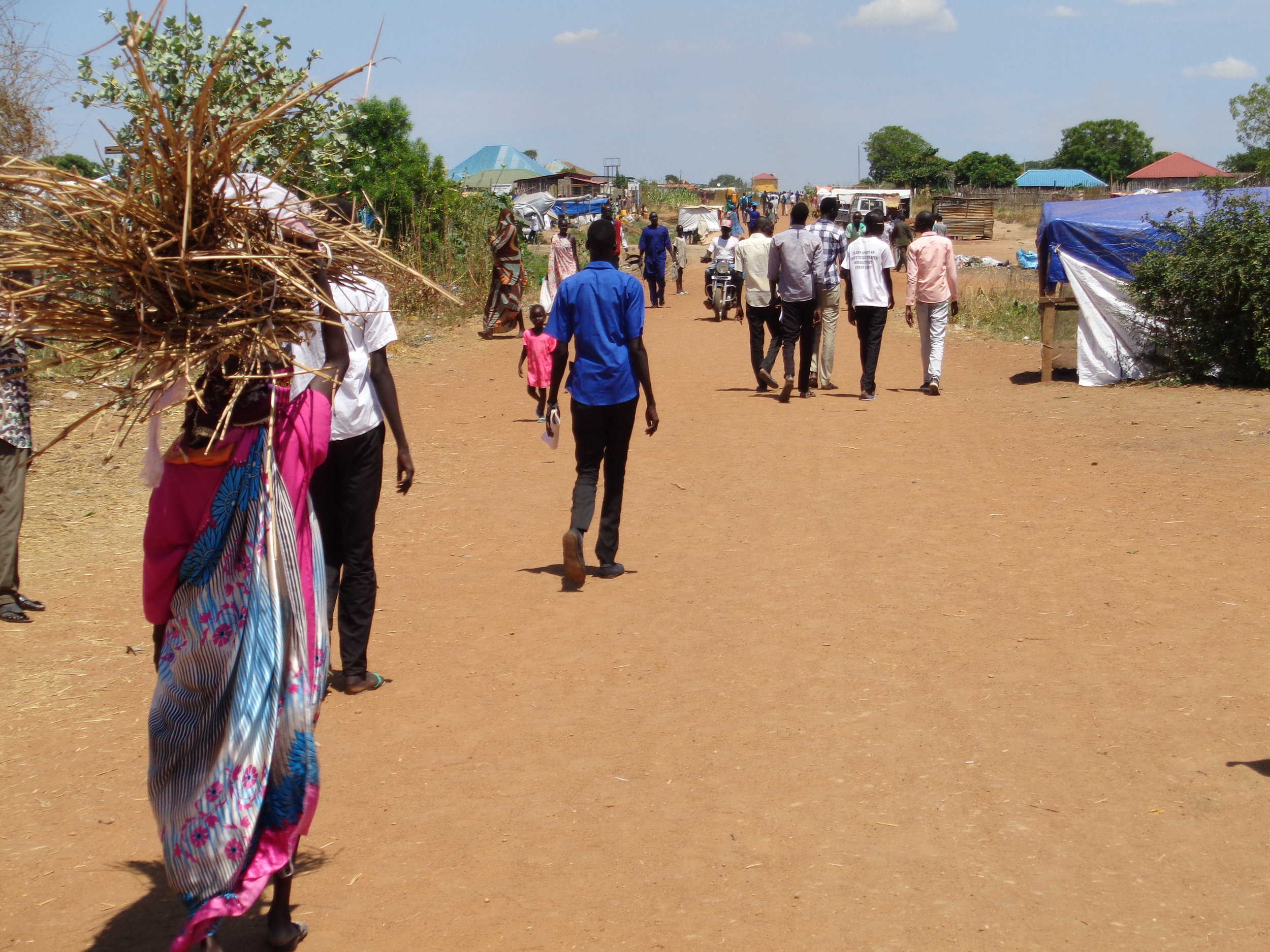 Us South Sudan Partnership On Deportee Repatriation
Apr 22, 2025
Us South Sudan Partnership On Deportee Repatriation
Apr 22, 2025 -
 La Palisades Wildfires Which Celebrities Lost Their Homes
Apr 22, 2025
La Palisades Wildfires Which Celebrities Lost Their Homes
Apr 22, 2025 -
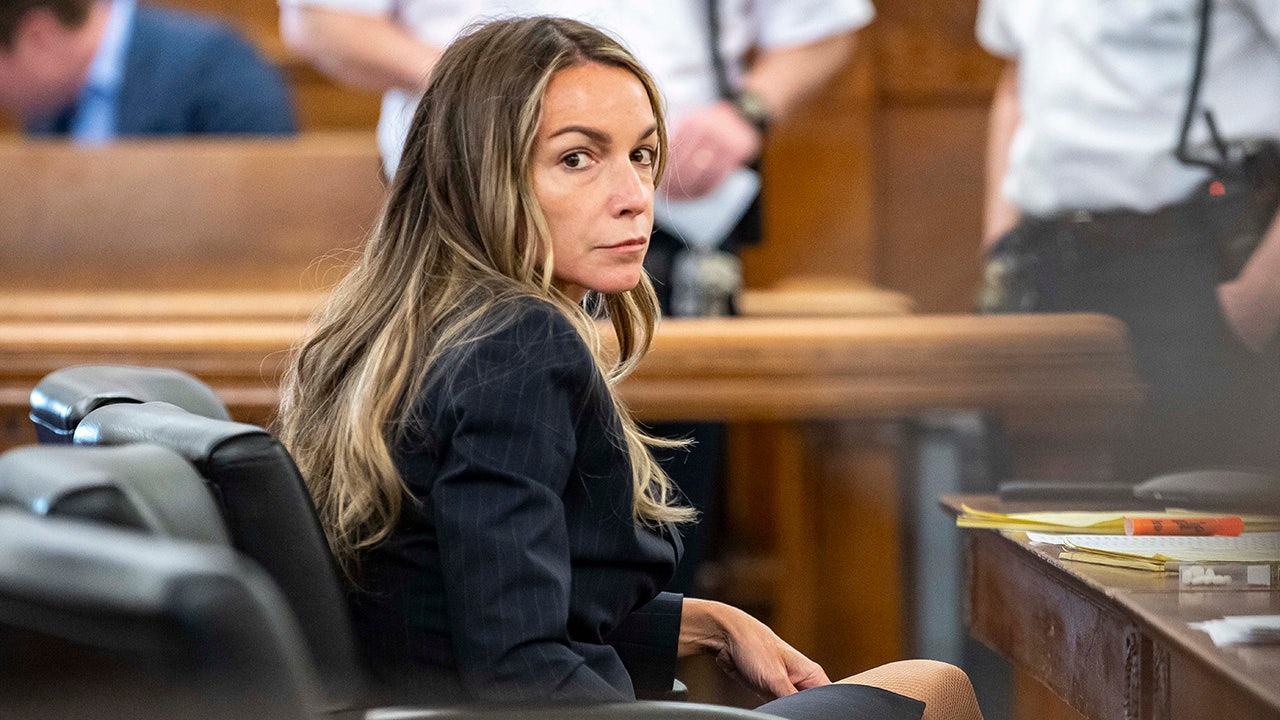 Chronology Of The Karen Read Murder Case From Arrest To Verdict
Apr 22, 2025
Chronology Of The Karen Read Murder Case From Arrest To Verdict
Apr 22, 2025
